The Importance and Methods of Textile Recycling
Textile recycling is an essential aspect of sustainability in today’s world, especially in the face of increasing waste generation and environmental degradation. With the fashion industry being one of the leading contributors to waste, recycling textiles offers a viable solution not only to mitigate environmental issues but also to promote circular economy principles.
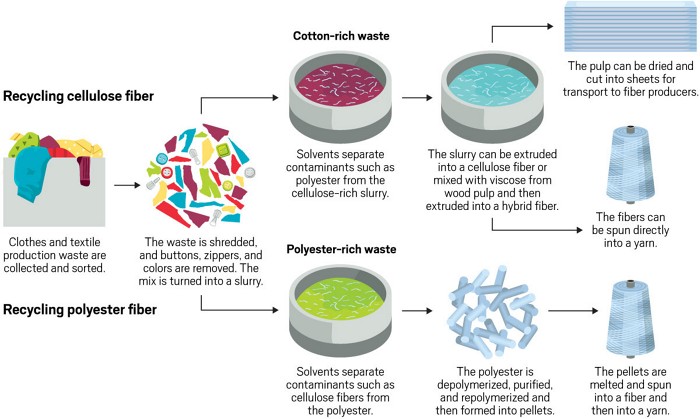
Transforming textiles.
Source: C&EN – American Chemical Society
As we delve into textile recycling, it is crucial to understand the processes involved and the benefits they bring. Textile recycling refers to the process of recovering fibers, yarns, or fabrics from used textiles and reprocessing them into new, useful products. This method can significantly reduce the amount of textile waste that ends up in landfills, contributing to pollution and waste management challenges.

Reasons for Recycling Textiles.
Source: New Haven Solid Waste & Recycling Authority
The Benefits of Textile Recycling
Recycling textiles offers numerous benefits:
- Environmental Protection: By recycling textiles, we can significantly reduce the demand for raw materials, thus decreasing the energy and resources needed for new textile production.
- Waste Reduction: Textile recycling diverts waste from landfills, reducing the environmental burden associated with decomposition.
- Economic Advantages: The recycling process creates job opportunities in the collection, sorting, and processing of textile waste while fostering local economies.
- Conservation of Resources: Recycling helps conserve water, energy, and natural resources, essential for the production of new textiles.
Methods of Textile Recycling
Several methods of textile recycling exist, each suited for different types of materials and products:
- Mechanical Recycling: This process involves shredding old fabrics into fibers, which can then be spun into yarn or used for other purposes, such as insulation or padding.
- Chemical Recycling: This technique breaks down textiles at a molecular level, allowing for the retrieval of individual fibers. A notable example includes the chemical recycling of polyester fabrics, which can be transformed back into raw polyester.
- Upcycling: Upcycling is a creative process where old textiles are transformed into new products. This process often involves crafting, sewing, and innovative design.
- Donation and Resale: Donating wearable clothes to charitable organizations or selling them in second-hand stores prolongs the life of textiles and keeps them out of landfills.

Recycling Fashion for a Better Future.
Source: Impacting Our Future
Challenges Facing Textile Recycling
Despite its benefits, textile recycling presents several challenges:
- Lack of Awareness: Many consumers are unaware of textile recycling methods and the importance of recycling, leading to low participation rates.
- Contamination: Mixed materials can complicate the recycling process, requiring more sophisticated technology and methods to separate different types of fabrics.
- Market Demand: The recycled textile market is not as developed as it could be, which can deter investments in recycling infrastructure.
Conclusion
As the consequences of textile waste become more pronounced, the urgency to promote and refine textile recycling methods grows. By increasing awareness and participation in recycling initiatives, we can ensure a sustainable future that conserves resources, reduces waste, and fosters economic resilience.
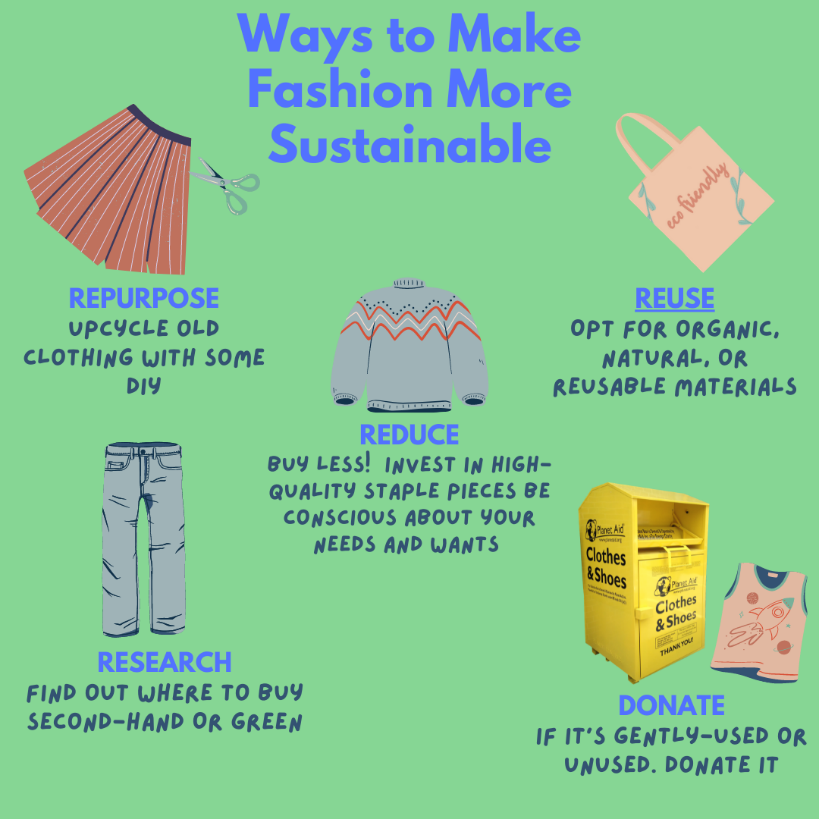
Understanding the importance of textiles.
Source: Planet Aid